ADAMAWA PLATEAU INITIATIVE (API)
ADAMAWA PLATEAU INITIATIVE (API)
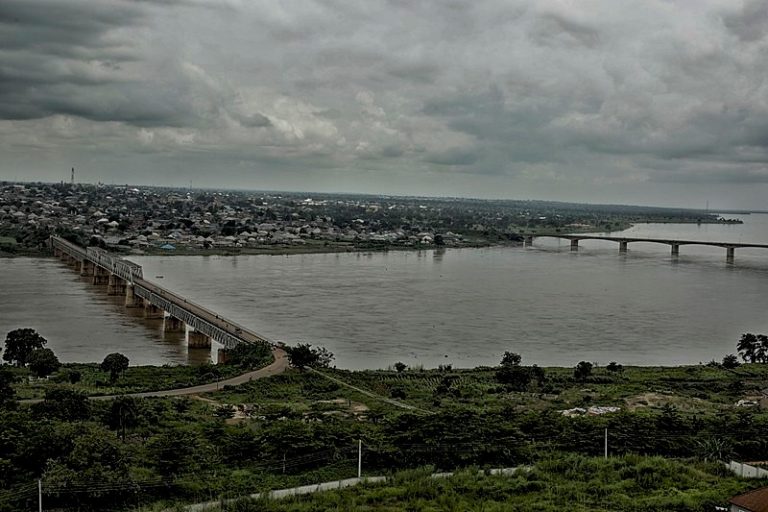
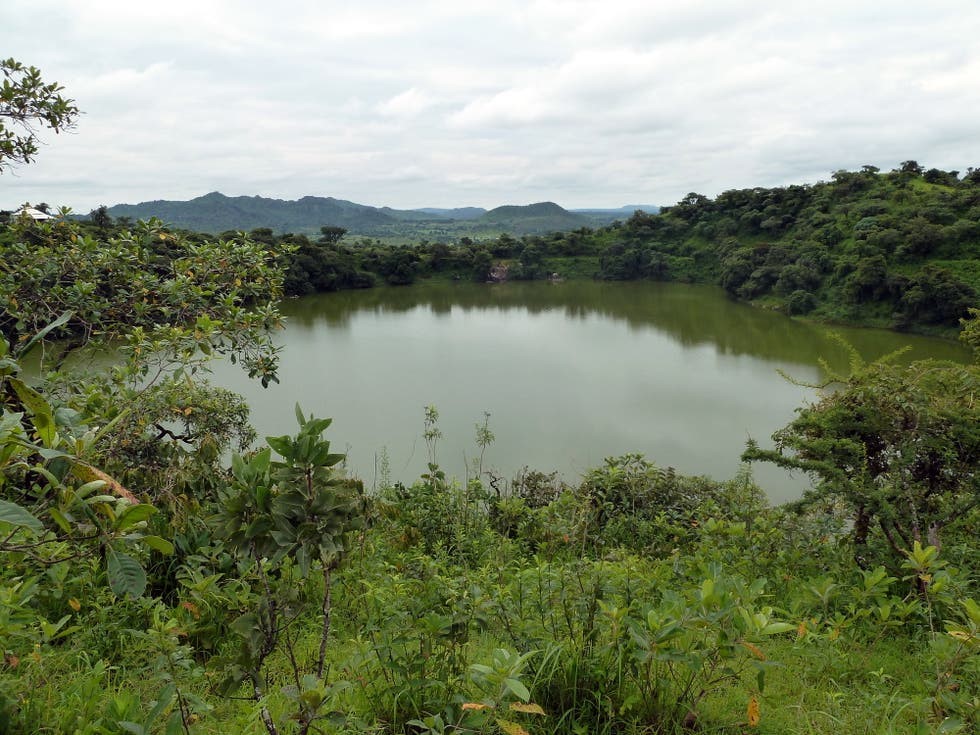
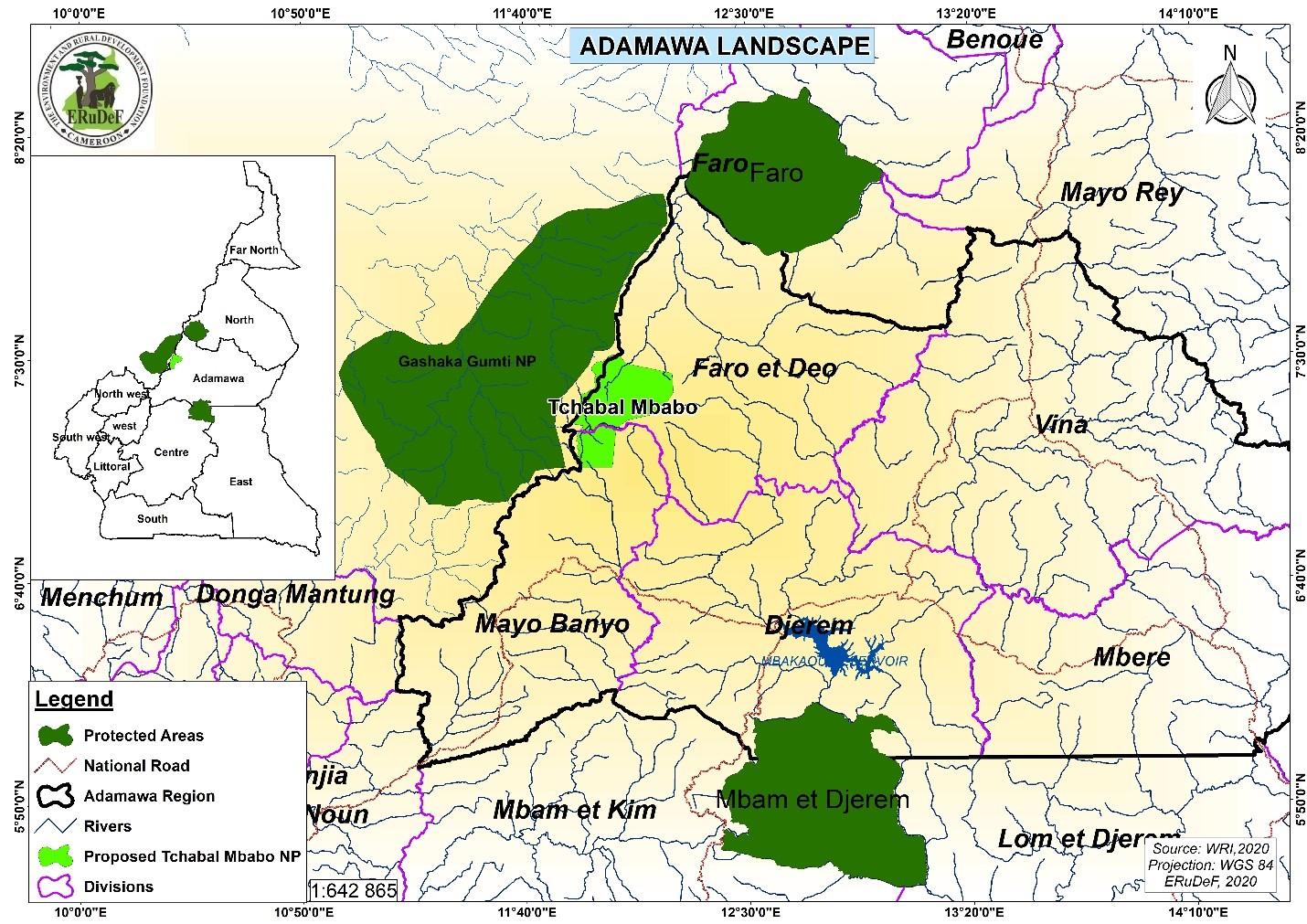
It is a project of Adamawa Plateau Initiative (API) which is a 15-year project that seeks to improve the livelihoods of poor farmers in the Adamawa plateau through landscape restoration and conservation of the biodiversity of the Tchabal Mbabo Mountains. Therefore, through this project, we can secure the economic future of these local people, while creating the local legal framework for long term sustainability and at the same time leading to a successful conservation of the forest ecosystem and biodiversity. The project will cover the five Divisions in the Adamawa Region (Vina, Mayo Banyo, Faro and Deo, Djérèm, Mbéré) with focus on the key watersheds and water catchments. The objectives of the project are; main objective: to support the ecological or green infrastructure of the Adamawa Plateau Landscape. Specific objectives: To characterize the watersheds of Adamawa Plateau, To characterize the water catchments and riparian forests of the main rivers flowing from Adamawa Plateau, To rebuild the surrounding Agricultural landscapes through sustainable agroforestry systems, To restore the degraded watershed and riparian forests through tree planting, to restore over 30,000 ha of degraded landscape of the Adamawa Plateau through the planting of 15 million trees for 15 years, and securing key biodiversity targets of the Tchabal Mbabo Mts including the gallery forests through the creation of Tchabal Mababo Reserve and management of the Mbere valley national park. Adamawa plateau is one of the most geologically and biologically diverse regions of Cameroon and so is often referred to as the “water tower” of Cameroon, since a large number of rivers of the country take their source in this region. The rivers of the Region flow into three different basins: the Niger River, Lake Chad, and the Atlantic Ocean. However, degradation caused by human pressures on resources through hunting, farming, livestock grazing, fuel wood extraction, uncontrolled bush fires, commercial bark harvesting, and chemical fishing seems to be a threat to the Adamawa Plateau watershed, therefore, through ecosystem restoration, the watershed will be conserved and will consequently serve its purpose of feeding about 15million Cameroonians. Furthermore, many important endemic and threatened species of both Flora; Prunus africana and Fauna; the threatened golden cat Felis aurata, leopard Panthera pardus and spotted hyena Crocuta Crocuta, and Elephants, inhabit this highland and will therefore be protected through this restoration project.